| |
Before
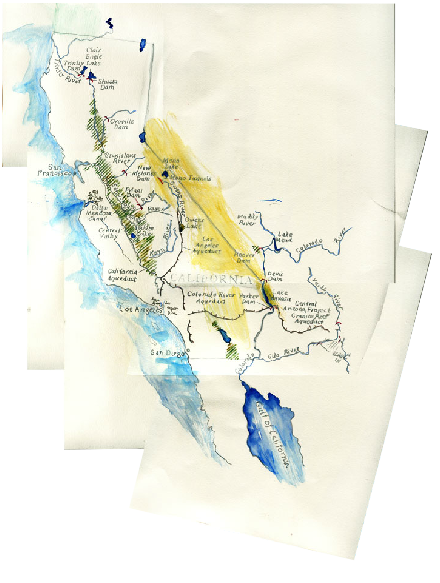
| Scant records suggest California's indigenous populations practice dry farming and water redirection. The Paiutes built temporary dams with boulders, brush and mud. Shallow ditches redirected water flow. RELATED PLACES Mono Lake, Mexicali, Calexico, California River Aqueduct |
Magic
| 1860 | The Climatology Theory, Rain Follows the Plow, takes hold, convincing Americans that the activity of agriculture will increase rainfall levels in the arid West. Supported by figures like Ferdinand Vandeveer Hayden, Samuel Aughey, and Charles Dana Wilbur who wrote: "God speed the plow.... By this wonderful provision, which is only man's mastery over nature, the clouds are dispensing copious rains ... [the plow] is the instrument which separates civilization from savagery; and converts a desert into a farm or garden.... To be more concise, Rain follows the plow." (citation) |
| 1890 | The War and Weather , By J Edward Powers, is published. Powers demonstrates that the ongoing Indian Wars are changing the climate of the American West. The noise of violence and genocide is increasing moisture, encouraging further colonization. |
| 1904 | Charles Hatfield, Rainmaker, successfully conjures a storm. Water will remain magical in Californian's consciousness.
RELATED PLACES San Joaquin Delta, Los Angeles, San Diego |
| 1848 | Gold is discovered at Sutter's Mill, CA |
| 1849 | The Gold Rush Prospectors redirect water with ditches and flumes. Levee construction begins at the Sacramento-San Joaquin Delta. The California Constitutional Convention directs the Surveyor General to study water management. RELATED PLACES San Joaquin Delta |
| 1851 | Brigham Young, sensing inevitable conflict with the American government, sends disciples cross the San Bernardinos. They begin to irrigate the arid basin now known as the Inland Empire. RELATED PLACES Inland Empire |
| 1871 | Luther and Eliza Tibbets bring two naval seedless oranges to Riverside, launching California's citrus industry. RELATED PLACES Inland Empire |
| 1884 | Valenicia Oranges Grown in San Bernardino go on display at World's Fair inspire thousands to move to Los Angeles, and the arid state of California. RELATED PLACES Inland Empire |
| 1887 | The Wright Act enables CA citizens to create local irrigation districts. |
Amnesia
| 1862 | Spring Valley Water Works Company establishes a monopoly on San Francisco Water. This will be the first of many corporations to advocate for the isolation of water from the landscape. Cement tubes, industrial waste and coffin-like walls eventually erase all memory of California's watershed connections. RELATED PLACES Bay Area, Salinas River |
| 1853 | Hydraulic Mining begins. River channels become increasing clogged with debris, increasing flooding. |
| 1869 | First transcontinental Railroad reaches the west. California begins exporting crops, increasing the need for agricultural water. |
| 1870 | Rudimentary Groundwater extraction begins. |
| 1905 | Colorado River Diversion Canals fail, forming the Salton Sea. |
| 1907 | After 3 years of careful maneuvering, William Mulholland gains control of the Owens Valley's water. RELATED PLACES Owens Lake, Los Angeles |
| 1908 | President Roosevelt approves San Francisco's request to hold the water rights for the Tuolomne River. RELATED PLACES Bay Area, Salinas River |
| 1912 | The first water flows from the Owens Valley into the San Fernando Valley. RELATED PLACES Owens Lake, Los Angeles |
| 1913 | Construction of the Los Angeles Aqueduct and pumping stations is complete. The Owens Valley is slowly drained of water. RELATED PLACES Owens Lake, Los Angeles |
| 1913 | John Muir and environmentalists lose the battle against Hetch Hetchy dam. RELATED PLACES Central Valley |
| 1940 | All-American Canal is completed, bringing Colorado River to Imperial and Coachella Valleys |
| 1950 | 80,000 pumps increase groundwater extraction. |
| 1962 -72 |
First Phase the State Water Project is completed (San Luis Reservoir, Castaic Lake, Lake Perris). RELATED PLACES Bay Area, Salinas River, Los Angeles |
| 1982 | Peripheral Canal Legislation, meant to address California Delta Salt Water intrusion while redirecting water to Southern CA, is repealed. |
Monuments
| 1902 | Congress Passes the Reclamation Act, so that irrigation projects can "reclaim" arid lands for human use. This was called "homemaking." "Water conservation" is defined as not allowing a drop of water to run, unused by humans, to the ocean. Over the next fifty years, dam building will fuel the economies and imaginations of Americans. These sublime marvels of human engineering symbolized American mastery over nature and manifest dominian over the West, and the world. |
| 1920 | The "Marshall Plan" for the Central Valley fails. RELATED PLACES Central Valley |
| 1922 | The Colorado River compact divides the waters of this wild river among seven states, enabling the widespread irrigation of the Southwest. RELATED PLACES Tijuana |
| 1928 | Congress authorizes the Boulder Canyon (Hoover Dam) Project. This is the first time large appropriations flow to the Bureau of Reclamation from the General fund. RELATED PLACES California River Aqueduct |
| 1928 | Mulholland's St Francis Dam collapses, killing over 400. RELATED PLACES Los Angeles |
| 1929 | The St Francis Dam disaster inspires a State Dam Safety program. |
| 1933 | Parker Dam construction for the LADWP Colorado River Aqueduct begins. RELATED PLACES Imperial Valley |
| 1936 | Federal Flood Control Act is passed. The era of multipurpose dams begins. |
| 1937 | WPA takes over the Central Valley project, which currently provides 4 million acre-feet of water to the agricultural users in the Central Valley. RELATED PLACES Central Valley |
| 1938 | Federal government begins construction on Shasta Lake and Dam. RELATED PLACES Shasta Dam |
| 1941 | Parker Dam Construction is complete, despite Arizona's threats of military action against the state. RELATED PLACES Mexicali, Calexico |
| 1948 | Construction on Folsom Dam begins.
RELATED PLACES San Joaquin Delta |
| 1955 | A record flood hits Northern and Central CA, spurring on the Feather River project at the Oroville site. RELATED PLACES San Joaquin Delta |
| 1961 | Construction Starts on the State Water Project and Agribusiness dominates the San Joaquin Valley. RELATED PLACES San Joaquin Delta |
| 1963 | Construction begins on the San Luis Reservoir and the California Aquaduct in the Delta. RELATED PLACES Bay Area, Salinas River |
| 1968 | Oroville Dam and Lake Oroville dedicated by Ronald Regan. RELATED PLACES San Joaquin Delta |
| 1972 | Edmonston Pumping Plant is dedicated. It lifts water nearly 2,000 feet up the Tehachapi Mountains. RELATED PLACES Central Valley |
| 1994 | Reclamation announces that "The arid West has essentially been reclaimed. " |
| 1994 | Reclamation shifts emphasis from construction to operation of existing facilities. |
Consciousness
| 1908- 1913 |
John Muir and Environmentalists fight against the construction of Hetch Hetchy Dam. RELATED PLACES Central Valley |
| 1928 | The CA Legislature mandates that water will not be wasted but put to "good and beneficial" uses. |
| 1960 | Voters approve the State Water Project, funding major transfers of water, and comprehensive state funding systems. |
| 1961 | The Davis-Dolwig Act is passed, directing the State Water Project to provide recreation, fish and wildlife enhancement. |
| 1966- 1982 |
Battles over the Peripheral Canal in Sacramento. RELATED PLACES San Joaquin Delta |
| 1967 | First Salmon and Steelhead fish enter the Feather River Fish Hatchery. RELATED PLACES San Joaquin Delta |
| 1968 | National Wild and Scenic Rivers Act becomes law. Skinner Fish facility begins operation. RELATED PLACES San Joaquin Delta |
| 1970 | California Environmental Quality Act and National Environmental Policy Art take effect. |
| 1972 | Federal Clean Water Act is passed. |
| 1983 | Public Trust doctrine invoked by court regarding Mono Lake. RELATED PLACES Mono Lake |
| 1984 | California Endangered Species Act is amended to protect both species and their critical habitat. |
| 1987 | 6-year drought begins. |
| 1988 | Winter-run Chinook Salmon is listed as a threatened species. |
| 1992 | California Valley Project improvement act is passed by congress, requiring 800,000 acre feed be dedicated for environmental use. |
| 1993 | Delta Smelt declared a threatened species. |
| 1994 | CALFED corporation is founded by state and federal agencies with management and regulatory responsibility in the Bay-Delta Estuary. |
| 1994 | Winter-run Chinook Salmon listed as an endangered species. |
| 1995 | Widespread flooding in California. |
| 1998 | Despite preparation for El Nino, flooding and levee failures in the Pajaro River and Suisun Marsh. RELATED PLACES Bay Area, Salinas River |
| 1998 | McPherrin Dam removed to restore chinook salmon in that Sacramento river tributary. RELATED PLACES central valley |
| 1999 | CALFED releases a document proposing long-term fix for the Bay-Delta. Spring run Chinook Salmon and Coastal Chinook Salmon listed at threatened specials. RELATED PLACES San Joaquin Delta |
| 2000 | CALFED's final report to focus on ecosystem restoration. Plans to commence with water conservation, water reclamation and groundwater recharge before new constructing new surface water projects. |
| 2009 | Oregon Senate Bill passed laying the groundwork for removal of four hydroelectric dams along the Klamath River to begin 2020. |
Bibliography